DynamoDB Stream, Lambda, and S3 - Local Setup
Introduction
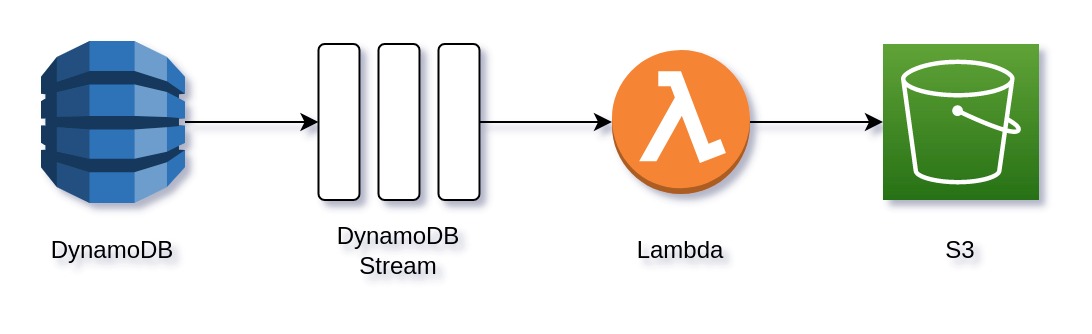
We’ll explore how you can create a simple application that implements DynamoDB Stream, Lambda function, and S3 in a local setup. The goal of this article is to show you how you can play with AWS services locally, explore their features, and build local tests for your application.
In order to follow the examples in this article you’ll need python, AWS CLI and Docker.
If you don’t have them already installed, please see:
We will see how to set up a connection between a DynamoDB Stream and a Lambda function that will process stream events and output results to an S3 bucket using localstack, which is a fully functional local cloud stack that let’s you easily develop and test your cloud and serverless applications locally.
There are multiple ways to approach this setup. In this article we will cover two of them:
- using AWS CLI and
- through code - AWS SDK for Python: boto3.
CLI
Run the localstack docker image using:
docker run --rm -it -p 4566:4566 -p 4571:4571 localstack/localstack
If everything goes well you should see INFO log stating:
Execution of "start_runtime_components" took XYZms. Now, that the
localstack is up and running we can create a DynamoDB table:
# AWS CLI requires the following parameters
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="something"
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="something"
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-west-1
aws dynamodb create-table \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--region=us-west-1 \
--billing-mode PAY_PER_REQUEST \
--table-name TestTable \
--attribute-definitions AttributeName=PartitionKey,AttributeType=S \
--key-schema AttributeName=PartitionKey,KeyType=HASH \
--stream-specification StreamEnabled=true,StreamViewType=NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES
To confirm that our table has been successfully created we can run:
aws dynamodb describe-table \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--region=us-west-1 \
--table-name=TestTable
and the output should look like:
{
"Table": {
"AttributeDefinitions": [
{
"AttributeName": "PartitionKey",
"AttributeType": "S"
}
],
"TableName": "TestTable",
"KeySchema": [
{
"AttributeName": "PartitionKey",
"KeyType": "HASH"
}
],
"TableStatus": "ACTIVE",
"CreationDateTime": "2022-02-27T18:17:38.893000+01:00",
"ProvisionedThroughput": {
"LastIncreaseDateTime": "1970-01-01T01:00:00+01:00",
"LastDecreaseDateTime": "1970-01-01T01:00:00+01:00",
"NumberOfDecreasesToday": 0,
"ReadCapacityUnits": 0,
"WriteCapacityUnits": 0
},
"TableSizeBytes": 0,
"ItemCount": 0,
"TableArn": "arn:aws:dynamodb:us-west-1:000000000000:table/TestTable",
"TableId": "193244b5-1713-4b0e-878f-aef94a1a707d",
"BillingModeSummary": {
"BillingMode": "PAY_PER_REQUEST",
"LastUpdateToPayPerRequestDateTime": "2022-02-27T18:17:38.893000+01:00"
},
"StreamSpecification": {
"StreamEnabled": true,
"StreamViewType": "NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES"
},
"LatestStreamLabel": "2022-02-27T17:17:38.893",
"LatestStreamArn": "arn:aws:dynamodb:us-west-1:000000000000:table/TestTable/stream/2022-02-27T17:17:38.893"
}
}
Next we will create an S3 bucket, using
create-bucket:
aws s3api create-bucket \
--region us-west-1 \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--bucket test-bucket
In order to use a Lambda function with DynamoDB Stream we first have to
create an IAM role and put role policy using:
create-role
and put-role-policy.
Creating role requires a trust relationship policy document in a JSON file:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
Then run the create_role command as:
aws iam create-role \
--region us-west-1 \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--role-name LambdaRole \
--path "/service-role/" \
--assume-role-policy-document file://trust-relationship.json
We need to add an inline policy document to the IAM role, this will require a policy document that will allow a Lambda function to access DynamoDB Stream, S3 and create logs in CloudWatch:
{
"Version": "2021-01-01",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "lambda:InvokeFunction",
"Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:us-west-1:0000000000:function:ddb_stream_listener*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:us-west-1:0000000000:*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:DescribeStream",
"dynamodb:GetRecords",
"dynamodb:GetShardIterator",
"dynamodb:ListStreams"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:us-west-1:0000000000:table/TestTable/stream/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:us-west-1:0000000000:test-bucket/*"
}
]
}
The following command will create an inline policy for the role:
aws iam put-role-policy \
--region us-west-1 \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--role-name LambdaRole \
--policy-name LambdaRolePolicy \
--policy-document file://role-policy.json
Since required policies are now in place, we can create a Lambda function handler that will log the event and create a file in the S3 bucket:
import os
import logging
import uuid
import json
import boto3
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
def handler(event, context):
"""Simple Lambda handler"""
logger.info('Event: %s', event)
try:
bucket_name = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"]
file_name = str(uuid.uuid4())
records = []
for record in event["Records"]:
records.append(json.dumps(record))
if records:
logger.info("Writing records to: %s", file_name)
logger.info("Number fo records: %d", len(records))
s3 = boto3.resource(
"s3",
endpoint_url='http://localhost:4566',
aws_access_key_id = 'something',
aws_secret_access_key = 'something'
)
s3.Bucket(bucket_name).put_object(Key=file_name, Body="\n".join(records))
except Exception as e:
logger.error("An error occured: %s", e)
In order to use this handler and upload it as a function we have to first zip
it and then create a lambda function using:
create-function
zip lambda_handler.zip lambda_handler.py
aws lambda create-function \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--function-name test-lambda-function \
--zip-file fileb://lambda_handler.zip \
--handler lambda_handler.handler \
--runtime python3.8 \
--environment Variables={BUCKET_NAME=test-bucket} \
--role arn:aws:iam::000000000000:role/LambdaRole
The only thing that is left is to create an event source mapping for the Lambda
function. For this we need the DynamoDB Stream ARN of our stream, which we can
get by listing DynamoDB Streams using:
list-streams
aws dynamodbstreams list-streams \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--table-name TestTable
you should see an output like:
{
"Streams": [
{
"StreamArn": "arn:aws:dynamodb:us-west-1:000000000000:table/TestTable/stream/2022-02-27T17:17:38.893",
"TableName": "TestTable",
"StreamLabel": "2022-02-27T17:17:38.893"
}
]
}
Now, we can create a source mapping using
create-event-source-mapping
aws lambda create-event-source-mapping \
--region us-west-1 \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--function-name test-lambda-function \
--event-source arn:aws:dynamodb:us-west-1:000000000000:table/TestTable/stream/2022-02-27T17:17:38.893 \
--batch-size 10 \
--starting-position TRIM_HORIZON
Finally, we can test the setup by inserting an item into DynamoDB table:
aws dynamodb put-item \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--table-name TestTable \
--item \
'{"PartitionKey": {"S": "random-key"}, "Value": {"S": "SomethingRandom"}}'
and if everything goes well you should see a file in the S3 bucket:
aws s3api list-objects \
--endpoint-url http://localhost:4566 \
--bucket test-bucket
Python
The same can be done through python code using boto3 service clients. First we define environment variables, clients and helper functions:
import os
import shutil
import json
import boto3
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = "something"
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = "something"
ENDPOINT_URL = "http://localhost:4566"
AWS_REGION = "us-west-1"
def read_policy_document(document):
with open(document, "r") as f:
policy_document = json.load(f)
return json.dumps(policy_document)
def get_boto3_client(service):
return boto3.client(
service,
region_name=AWS_REGION,
endpoint_url=ENDPOINT_URL
)
s3_client = get_boto3_client("s3")
ddb_client = get_boto3_client("dynamodb")
lambda_client = get_boto3_client("lambda")
iam_client = get_boto3_client("iam")
ddb_streams_client = get_boto3_client("dynamodbstreams")
then for each service we create functions that will do the same as AWS CLI commands.
DynamoDB:
def create_dynamodb_table(table_name):
"""Creates a DynamoDB table with stream enabled"""
return ddb_client.create_table(
TableName=table_name,
KeySchema=[
{
'AttributeName': 'PartitionKey',
'KeyType': 'HASH',
}
],
AttributeDefinitions=[
{
'AttributeName': 'PartitionKey',
'AttributeType': 'S',
}
],
StreamSpecification={
'StreamEnabled': True,
'StreamViewType': 'NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES',
},
)
def get_dynamodb_stream_arns(table_name):
"""Gets DynamoDB Stream ARNs for a table"""
response = ddb_streams_client.list_streams(
TableName=table_name
)
return [x["StreamArn"] for x in response["Streams"]]
S3:
def create_s3_bucket(name):
"""Creates an S3 bucket"""
return s3_client.create_bucket(
Bucket=name,
)
IAM:
def create_iam_role(role, document):
"""Creates an IAM role"""
return iam_client.create_role(
RoleName=role,
AssumeRolePolicyDocument=read_policy_document(document)
)
def put_role_policy(role, policy, document):
"""Adds or updates an inline policy document that is embedded in
the specified IAM role.
"""
return iam_client.put_role_policy(
RoleName=role,
PolicyName=policy,
PolicyDocument=read_policy_document(document)
)
and Lambda:
def create_lambda_funcion(name, role, function, env_variables):
"""Creates a Lambda function"""
shutil.make_archive(function, "zip", ".", f"{function}.py")
with open(f"{function}.zip", "rb") as f:
zipped_code = f.read()
return lambda_client.create_function(
FunctionName=name,
Runtime='python3.8',
Role=role['Role']['Arn'],
Handler=f'{function}.handler',
Code=dict(ZipFile=zipped_code),
Environment={
'Variables': env_variables
},
)
def create_lambda_event_source_mapping(function, source):
return lambda_client.create_event_source_mapping(
FunctionName=function,
EventSourceArn=source,
)
Finally, we can combine all of them and create the application:
def main():
create_s3_bucket(name="test-bucket")
create_dynamodb_table(table_name="TestTable")
stream_arn = get_dynamodb_stream_arns("TestTable")[0]
role = create_iam_role(
role="LambdaRole",
document="trust-relationship.json"
)
put_role_policy(
role="LambdaRole",
policy="LambdaRolePolicy",
document="role-policy.json"
)
create_lambda_funcion(
name="TestLambda",
role=role,
function="lambda_handler",
env_variables={"BUCKET_NAME": "test-bucket"}
)
create_lambda_event_source_mapping(
function="TestLambda",
source=stream_arn
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
The only thing that is left is to test it and see if we get what we expect. We first insert a new item in the DynamoDB table then wait for the DynamoDB Stream and the Lambda function to process the event and finally read from an S3 file.
import os
import time
from pprint import pprint
import json
import boto3
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = "something"
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = "something"
ENDPOINT_URL = "http://localhost:4566"
AWS_REGION = "us-west-1"
def get_boto3_client(service):
return boto3.client(
service,
region_name=AWS_REGION,
endpoint_url=ENDPOINT_URL
)
s3_client = get_boto3_client("s3")
ddb_client = get_boto3_client("dynamodb")
def main():
ddb_client.put_item(
TableName="TestTable",
Item= {
"PartitionKey": {"S": "test-key"},
"Value": {"S": "test-value"},
},
)
time.sleep(2) # wait for the stream and lambda
ddb_client.scan(
TableName="TestTable"
)
s3_objects = s3_client.list_objects(
Bucket="test-bucket",
)
item_key = s3_objects["Contents"][0]["Key"]
s3_file = s3_client.get_object(Bucket="test-bucket", Key=item_key)
pprint(json.loads(s3_file["Body"].read().decode("utf-8")))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
The output should look like:
{'awsRegion': 'us-west-1',
'dynamodb': {'ApproximateCreationDateTime': 1646044849.2324855,
'Keys': {'PartitionKey': {'S': 'test-key'}},
'NewImage': {'PartitionKey': {'S': 'test-key'},
'Value': {'S': 'test-value'}},
'SequenceNumber': '1',
'SizeBytes': 65,
'StreamViewType': 'NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES'},
'eventID': 'c4b9cd19',
'eventName': 'INSERT',
'eventSource': 'aws:dynamodb',
'eventSourceARN': 'arn:aws:dynamodb:us-west-1:000000000000:table/TestTable',
'eventVersion': '1.1'}
which is what we expected.
Leave a comment